Run a Cron Job Continuous Reboot
Introduction The Cron daemon is a Linux utility used for scheduling system tasks and processes. It uses cron tables (crontab) to store and read scheduled jobs. This tutorial will cover how you can use crontab to schedule jobs to be run at system reboot. Prerequisites With the Open the cron task list by using the following command: If you have multiple text editors installed, the system prompts you to select an editor to update the cron task list with. Use the number in the brackets to choose your preferred option. We will be using the default option, Nano. Note: Leaving the field blank and pressing enter chooses the first option available. To run a cron job at every system boot, add a string called Use the following syntax when adding a Note: Always use the full path to the job, script, or command you want to run, starting from the root. Press For example, if we wanted to have the system date written in a file called date.txt when Linux restarts, we would add the following string: If we wanted to run the backup shell at reboot, we would add: Note: In some cases, the crond service needs to be enabled on boot for the configuration to function. To enable this service, use: To run a job with a delay after the system reboots, use the sleep command when adding the If you want to create a text file with the system date five minutes after reboot, add: Each To do this, open the task list using the To remove a task from the list, delete the appropriate line from the appropriate string. Press Note: Learn more about the Linux at command, the alternative for cron job for scheduling jobs. Conclusion After following this tutorial, you understand how to use crontab to schedule jobs to run at system reboot. For more ways to schedule jobs in crontab, check out our guide to setting up cron jobs. Was this article helpful? Yes No 
Crontab Command Overview
crontab command, you have full control of when and how jobs are executed. Use crontab to set job execution time down to the minute, without the need for looping and timing logic in the task.crontab has low resource requirements since it doesn't reserve system memory when it isn't running.Crontab on Boot: Run a Cron Job at Boot Time
crontab -e 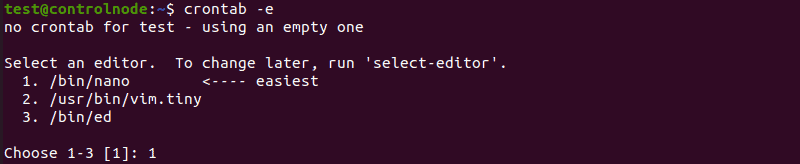
@reboot to the end of the task list. The job defined by this string runs at startup, immediately after Linux reboots.@reboot string:
@reboot [path to command] [argument1] [argument2] … [argument n] @reboot [part to shell script] Control + X to exit Nano, then Y and Enter to save any changes you made.
@reboot date >> ~/date.txt
@reboot /root/backup.sh 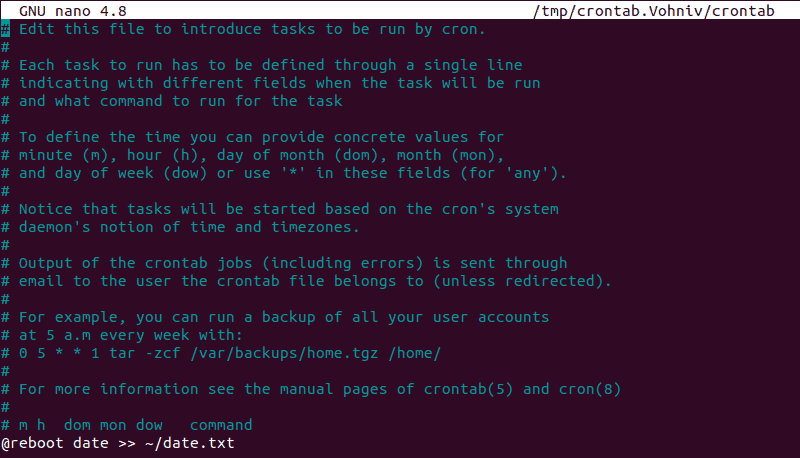
To check if the crond service is enabled, use:
sudo systemctl status cron.service
sudo systemctl enable cron.service Run a Cron Job at Boot With Delay
@reboot string:
@reboot sleep [time in seconds] && [path to job]
@reboot sleep 300 && date >> ~/date.txt Remove a Reboot Command
@reboot string you add to the cron task list runs a job every time Linux restarts. If you no longer wish to run a job, remove it from the task list.crontab -e command. Scroll down to the bottom to review the jobs you added.Control + X to exit Nano, then Y and Enter to save changes.
Aleksandar Kovačević
With a background in both design and writing, Aleksandar Kovacevic aims to bring a fresh perspective to writing for IT, making complicated concepts easy to understand and approach.
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/crontab-reboot
0 Response to "Run a Cron Job Continuous Reboot"
Post a Comment